Knee Replacement Surgery
When a knee is so severely damaged by disease or injury, an artificial knee replacement may be considered. During knee replacement surgery, joint surfaces are substituted or replaced by prostheses. Nearly 600,000 knee replacement surgeries are performed annually in the U.S. The most common age for knee replacement is between 60 years old and 80 years old.
For more information on joint replacement or to meet with an orthopedic surgeon, call Christian Hospital at 314.747.9355 or email us.
When is a Knee Replacement Needed?
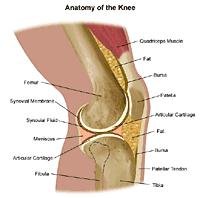
Click Image to Enlarge
The most common condition that results in the need for knee replacement surgery is osteoarthritis, a degenerative, joint disease that affects mostly middle-aged and older adults. Osteoarthritis is characterized by the breakdown of joint cartilage and adjacent bone in the knees. Other forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis and arthritis that results from a knee injury can also lead to degeneration of the knee joint. In addition, fractures, torn cartilage, and/or torn ligaments also can lead to irreversible damage to the knee joint over the years.
The decision to replace the painful knee with an artificial one is a joint decision between you and your doctor. Other alternative treatments may first be used, including assistive walking devices, anti-inflammatory medications, injections, and bracing.
For more information on joint replacement or to meet with an orthopedic surgeon, call Christian Hospital at 314.747.9355 or email us.
How is a Knee Replaced with an Artificial Knee?
Although each procedure varies, generally, surgery to replace a knee usually lasts about two hours. After the damaged bone and cartilage of the knee is removed, the orthopedic surgeon will place the new artificial knee in its place.
The most common type of knee prostheses used in replacement surgery is cemented prosthesis. Uncemented prosthesis is not commonly used. Sometimes, a combination of the two types is used to replace a knee. A knee prosthesis is made up of metal with ceramic and/or plastic. A cemented prosthesis is attached to the bone with a type of epoxy. An uncemented prosthesis attaches to the bone with a fine mesh of holes on the surface, in order for the bone to grow into the mesh and attach naturally to the prosthesis.
The artificial knee is comprised of the following three components:
-
Tibial component (to replace the top of the tibia, or shin bone)
-
Femoral component (to replace the two femoral [thighbone] condyles and the patella groove)
-
Patellar component (to replace the bottom surface of the kneecap that rubs against the thighbone)
While undergoing surgery, the patient may be under general anesthesia or awake with spinal or epidural anesthesia.
For more information on joint replacement or to meet with an orthopedic surgeon, call Christian Hospital at 314.747.9355 or email us.
After Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgeries usually require an in-hospital stay of several days. Even while in the hospital, the patient usually begins physical therapy exercises to begin regaining range of motion in the knee. Physical therapy will continue at home. Pain medication also will be administered to keep the patient comfortable.
The incision will have stitches or staples that will be removed after a few weeks.
For more information on joint replacement or to meet with an orthopedic surgeon, call Christian Hospital at 314.747.9355 or email us.